사인법칙, 제1코사인법칙, 제2코사인법칙
사인법칙
사인법칙은 삼각형에서 사인 값과 변의 길이 사이의 관계를 나타낸 공식입니다. 원에 내접하는 삼각형을 이용하여 공식을 유도합니다.
다음과 같이 반지름의 길이가 $ \mathrm{R} $인 원 위에 삼각형 $ \mathrm{ABC} $를 그리고, 변 $ \mathrm{BC} $를 $ a $라고 하겠습니다.
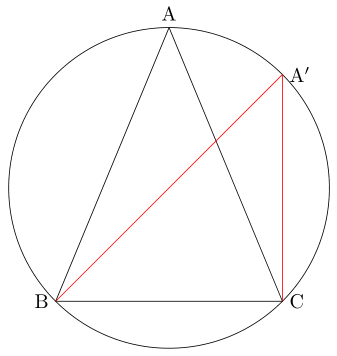
점 $ \mathrm{B} $를 지나는 지름을 긋고 그 지름의 반대편 끝을 $ \mathrm{A'} $이라고 하면, 삼각형 $ \mathrm{A'BC} $는 $ \mathrm{\angle C} $가 직각인 직각삼각형이 됩니다.
$ \mathrm{\angle A} $와 $ \mathrm{\angle A'} $은 호 BC에 대한 원주각이므로 각의 크기가 같습니다. 따라서 $ \sin \mathrm{A} $와 $ \sin \mathrm{A'} $의 값도 같습니다.
\begin{gather*}
\sin \mathrm{A} = \sin \mathrm{A'} = \frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{A'B}} = \frac{a}{\mathrm{2R}}
\end{gather*}
이므로
\begin{gather*}
\frac{a}{\sin \mathrm{A}} = \mathrm{2R}
\end{gather*}
이 성립합니다.
다음처럼 $ \mathrm{\angle A} $가 직각이라면 $ \mathrm{\sin A} = 1 $입니다.
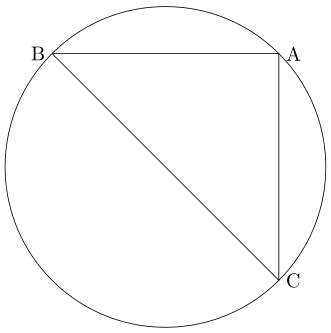
변 $ \mathrm{BC} $가 원의 지름이자 $ a $이므로
\begin{gather*}
\mathrm{\sin A} = 1 = \frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{BC}} = \frac{a}{\mathrm{2R}}
\end{gather*}
이고
\begin{gather*}
\frac{a}{\sin \mathrm{A}} = \mathrm{2R}
\end{gather*}
이 성립합니다.
다음은 $ \mathrm{\angle A} $가 둔각인 경우입니다. 점 $ \mathrm{B} $를 지나는 지름을 긋고 그 지름의 반대편 끝을 $ \mathrm{A'} $이라고 하면, 삼각형 $ \mathrm{A'BC} $는 $ \mathrm{\angle C} $가 직각인 직각삼각형이 됩니다.
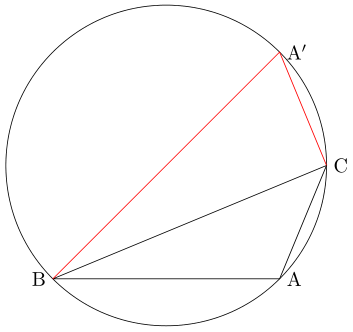
사각형 $ \mathrm{A'BAC} $는 원에 내접하므로 대각의 합이 $ \mathrm{\pi} $입니다. 따라서 $ \mathrm{A} = \pi - \mathrm{A'} $이고
\begin{gather*}
\sin \mathrm{A} = \sin ( \pi - \mathrm{A'} ) = \sin \mathrm{A'} = \frac{\mathrm{BC}}{\mathrm{A'B}} = \frac{a}{\mathrm{2R}}
\end{gather*}
이므로
\begin{gather*}
\frac{a}{\sin \mathrm{A}} = \mathrm{2R}
\end{gather*}
이 성립합니다.
즉 $ \dfrac{a}{\sin \mathrm{A}} = \mathrm{2R} $는 $ \mathrm{\angle A} $가 예각, 직각, 둔각일 때 다 성립합니다. 또한 $ \mathrm{\angle B} $, $ \mathrm{\angle C} $에 대해서도 성립하므로 다음의 등식이 만들어집니다.
\begin{gather*}
\frac{a}{\sin \mathrm{A}} = \frac{b}{\sin \mathrm{B}} = \frac{c}{\sin \mathrm{C}} = \mathrm{2R}
\end{gather*}
이를 사인법칙이라고 합니다.
제1코사인법칙
삼각형 $ \mathrm{ABC} $의 꼭짓점 $ \mathrm{A} $에서 변 $ \mathrm{BC} $에 수선의 발을 $ \mathrm{D} $라고 하겠습니다.
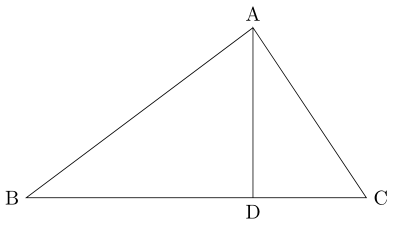
$ \mathrm{CD} $와 $ \mathrm{BD} $의 길이는
\begin{gather*}
\mathrm{CD = CA \cos C, \ \ BD = AB \cos B}
\end{gather*}
이고, $ \mathrm{BC = CD + BD} $이므로
\begin{gather*}
\mathrm{BC = CA \cos C + AB \cos B}
\end{gather*}
입니다. $ \mathrm{BC}=a $, $ \mathrm{CA} = b $, $ \mathrm{AB} = c $라 하면
\begin{gather*}
a = b \cos \mathrm{C} + c \cos \mathrm{B}
\end{gather*}
로 나타낼 수 있는데, 이를 제일코사인법칙이라고 합니다. $ \mathrm{\angle A} $가 둔각일 때만 증명했으나, 직각, 예각일 때도 성립합니다.
마찬가지 방식으로
\begin{gather*}
b = c \cos \mathrm{A} + a \cos \mathrm{C}, \ \ c = a \cos \mathrm{B} + b \cos \mathrm{A}
\end{gather*}
도 성립합니다.
제2코사인법칙
제일코사인법칙은 다음과 같습니다.
\begin{gather*}
a = b \cos \mathrm{C} + c \cos \mathrm{B}, \ \ b = c \cos \mathrm{A} + a \cos \mathrm{C}, \ \ c = a \cos \mathrm{B} + b \cos \mathrm{A}
\end{gather*}
양변에 $ a $, $ b $, $ c $를 각각 곱하면
\begin{gather*}
a^2 = ab \cos \mathrm{C} + ca \cos \mathrm{B}, \ \ b^2 = bc \cos \mathrm{A} + ab \cos \mathrm{C}, \ \ c^2 = ca \cos \mathrm{B} + bc \cos \mathrm{A}
\end{gather*}
이고, $ a^2 - b^2 - c^2 $을 구하면
\begin{align*}
a^2 - b^2 - c^2 &= ab \cos \mathrm{C} + ca \cos \mathrm{B} - ( bc \cos \mathrm{A} + ab \cos \mathrm{C} ) - ( ca \cos \mathrm{B} + bc \cos \mathrm{A} ) \\
&= -2bc \cos \mathrm{A}
\end{align*}
이고, 이를 정리하면
\begin{gather*}
a^2 = b^2 + c^2 -2bc \cos \mathrm{A}
\end{gather*}
입니다. 이를 제이코사인법칙이라고 합니다.
마찬가지 방식으로
\begin{gather*}
b^2 = c^2 + a^2 -2bc \cos \mathrm{B}, \ \ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 -2bc \cos \mathrm{C}
\end{gather*}
가 성립합니다.